Chips are born in a pcb diamond cutter factory, a place that specializes in crafting semiconductor wafers into individual units. The refined art of turning a wafer into chips is known as “dicing”, and the facility houses multiple saws to complete the task. Carefully guided by trained personnel, each saw slices delicately through the thin substrate and creates discrete pieces with precision accuracy.
A profusion of pcb diamond cutter manufacturing centers now dot the Asian landscape, particularly spiking in China in recent years. Thanks to a generous investment from the Chinese government, the semiconductor industry has flourished as evidenced through the proliferation of these factories.
Financially, implementing a diamond cutting facility for PCBs can be a challenge; consequently, only well-funded corporations typically possess the resources to cover the required saws and the associated expenses. Establishing such a factory requires a major investment that many lack the capacity to achieve.
Head honchos in the space of pcb diamond cutters include ASML, a Dutch giant; Disco, an esteemed Japanese organization; and Applied Materials, an American authority.
The pcb diamond cutter sector is incredibly competitive, meaning manufacturers must find ways to stay ahead of the game with their innovative technology and expansive market reach. A key method used to improve efficiency is large investments in research and development that are geared towards discovering more advanced and effective methods for cutting semiconductor wafers.
With heightened demands for semiconductor chips on the horizon, the future of the pcb diamond cutter industry shines with promise. Companies that rise to the challenge of developing and employing cutting-edge technology will be in an advantageous position to capitalize on the sector’s growth.
Related Product
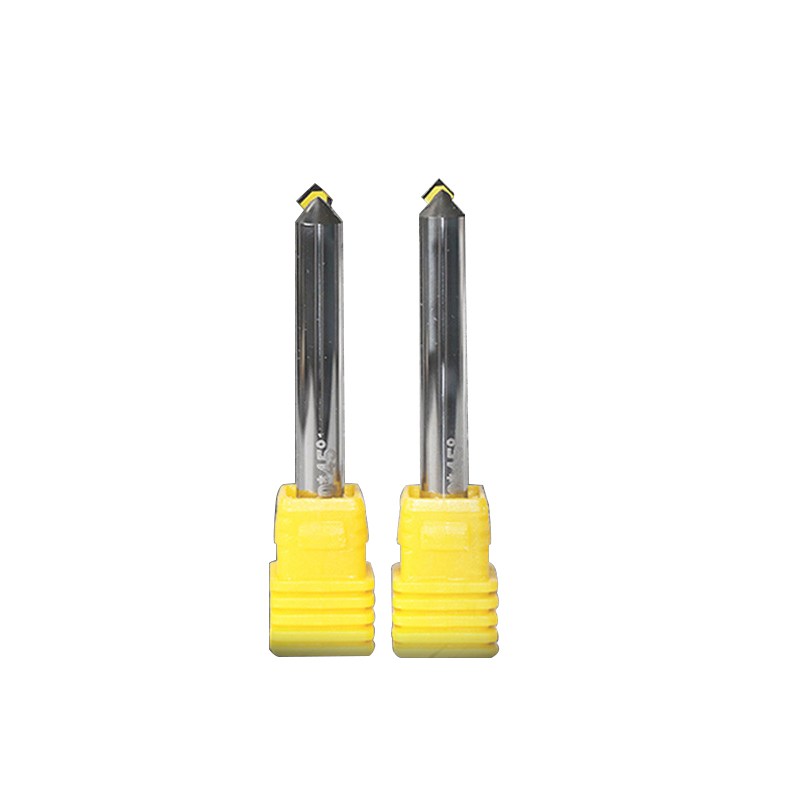

MCD Polishing Cutter for Gold Silver
Product Information Origin Tianjing, China Whether To Coat Uncoated Brand MSK Unit Weight 0.3kg Tool material Tungsten steel bar imported from Germany Product Size Shank Dia […]
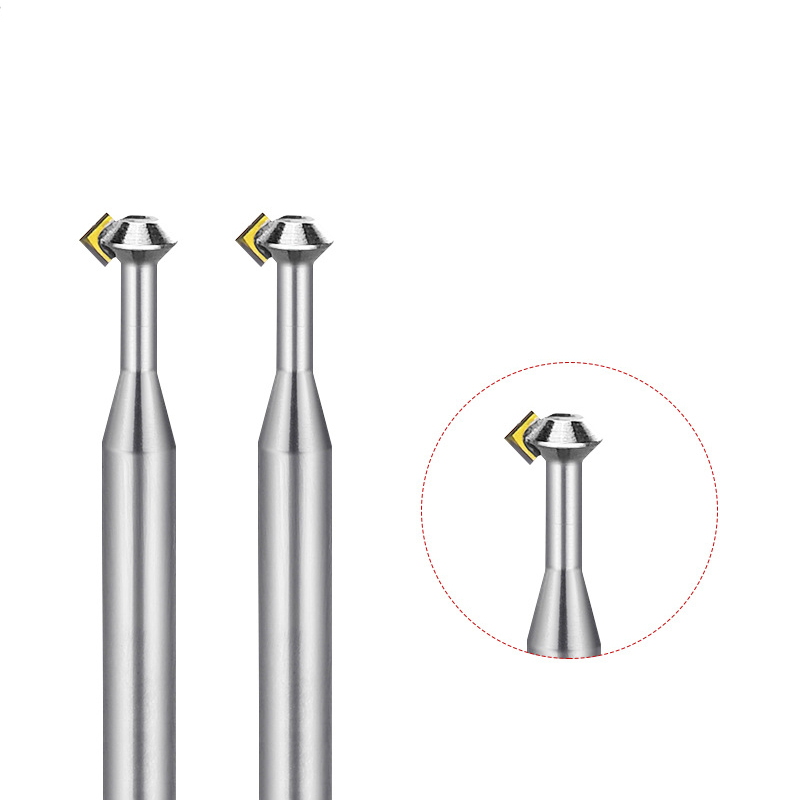
MCD High Gloss Chamfer Cutter For Gold
Product Information Origin Tianjing, China Type Flat Milling Cutter Brand Msk Whether To Coat Uncoated Series Cutter Milling Cutter Processing Range Clocks And Watches, Copp […]
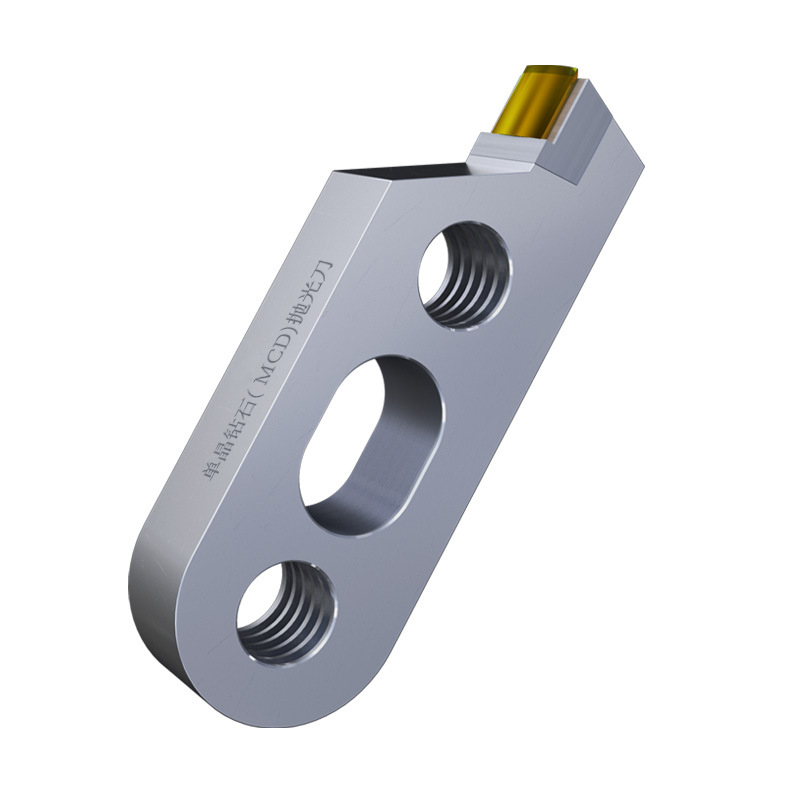

Single Crystal Diamond Polishing Cutter
Origin Tianjing, China Shank Diameter 6 (mm) Brand MSK Blade Change Method The Diamond Is Welded To The Cutter Body As A Whole Material Single Crystal Diamond (MCD) Scope Of […]
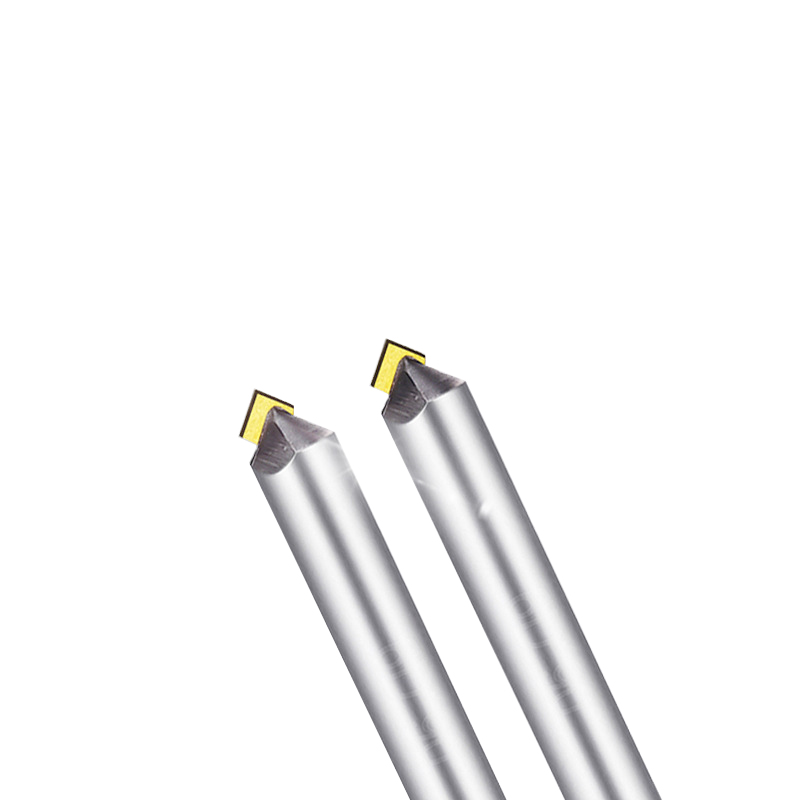
Lathe Bits MCD High Gloss Chamfer Tool
Product Information Origin Tianjing, China Cutting Edge Form Straight Edge Brand MSK Material Single Crystal Diamond Chamfer Angle 30°-180° Type Angle Milling Cutter Minimum […]
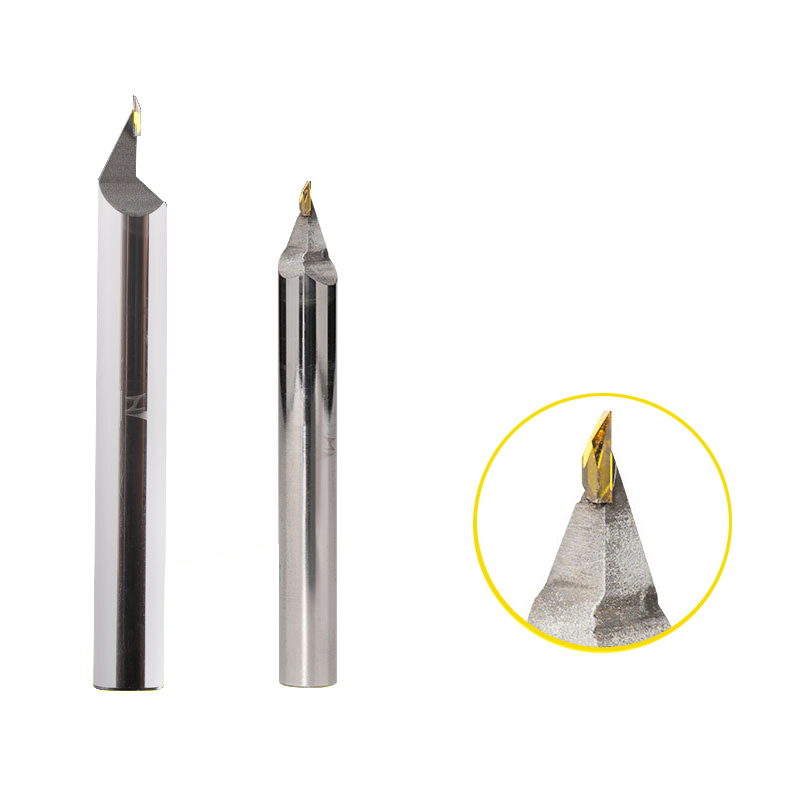

CVD/PVD/MCD Gold Jewelry Diamond Engraving Cutter
Parameter Product Name Single Crystal Diamond Carving Cutter Rotating Speed 10000-30000r/min Tool Nose Width 0.1-6.0mm Feed 1500-5000mm/min Blade Material Single Crystal Dia […]
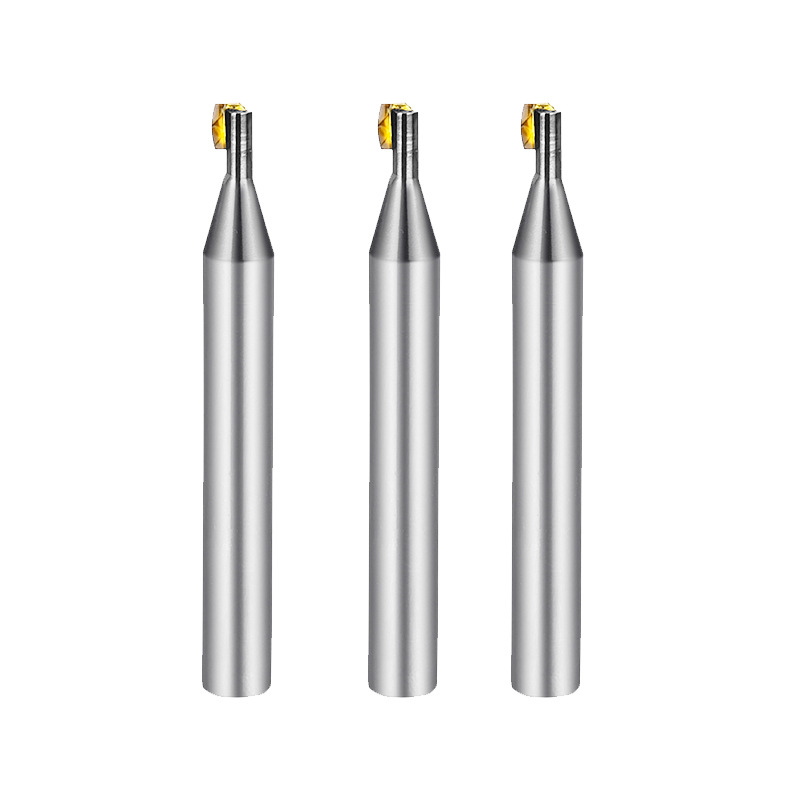

Diamond Turning Tools Outer Jewelry R Cutter
Product Information Origin Tianjing, China Material Tungsten Steel Brand Msk Type Half Round Key Milling Cutter Product Name Single Crystal Diamond Side Edge Arc Milling Cut […]
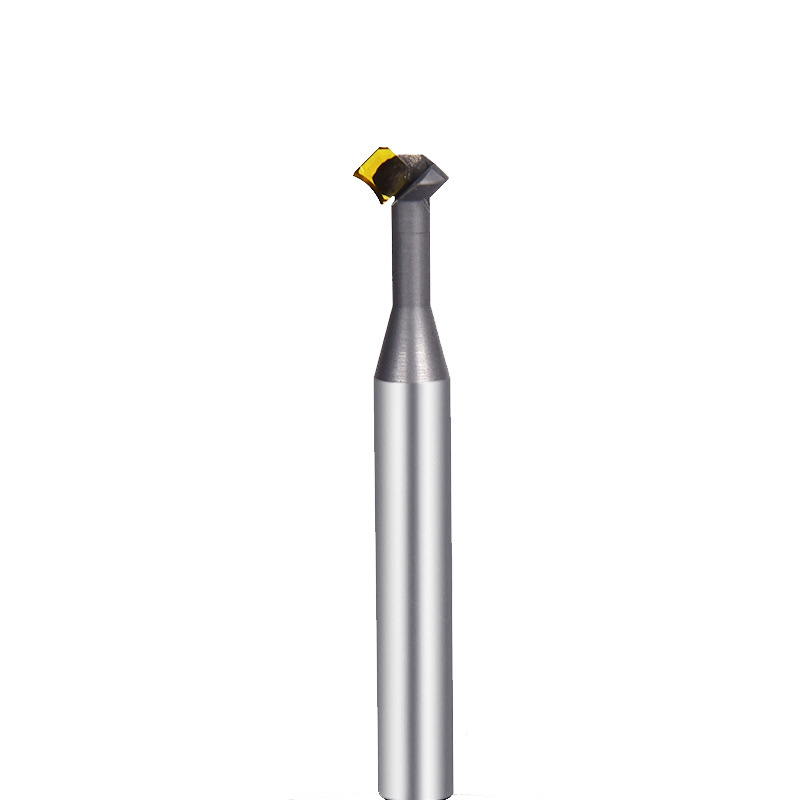

MCD Turning Tool Mirrow Finish R Cutter
Product Information Product Name Single Crystal Diamond Lower Chamfering Inner R Cutter Brand MSK Handle Material Tungsten Steel Blade Material Customized Pcd, Single Crysta […]
Post time: 2023-06-24




